Vaginitis and pelvic inflammatory diseases
Vaginitis and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) are two distinct but related conditions that gynecologists diagnose, treat, and manage to ensure women's reproductive health and well-being.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis refers to inflammation or infection of the vagina, often resulting from an imbalance in vaginal flora or an infection by bacteria, yeast, or other pathogens. Common types include bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis (yeast infection), and trichomoniasis.
Gynecological Services:
- Diagnosis: Conducting a pelvic examination to assess vaginal discharge, pH levels, and appearance of the vaginal walls.
- Laboratory Tests: Collecting samples for microscopic analysis, pH testing, and cultures to identify the specific cause of vaginitis (bacterial, fungal, or parasitic).
- Treatment: Prescribing appropriate medications such as antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal agents for yeast infections, or antiparasitic medications for trichomoniasis.
- Education: Providing information on hygiene practices, safe sex practices, and strategies to prevent recurrence of vaginitis.
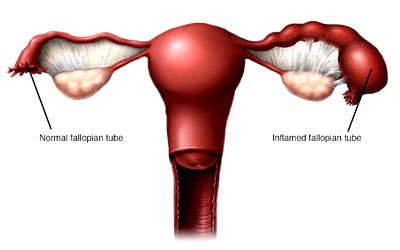
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs, typically caused by sexually transmitted bacteria spreading from the vagina or cervix to the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. Untreated, PID can lead to serious complications such as chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
Gynecological Services:
- Diagnosis: Evaluating symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, fever, and pain during intercourse. Conducting pelvic examination to check for tenderness, abnormal vaginal discharge, and signs of infection.
- Laboratory Tests: Performing tests to detect sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, which are common causes of PID. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess inflammation and infection markers.
- Imaging Studies: Utilizing ultrasound or other imaging techniques to assess the extent of pelvic inflammation and potential complications.
- Treatment: Administering antibiotics to treat the underlying infection, often requiring hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics in severe cases. Partner notification and treatment may also be recommended to prevent reinfection.
- Follow-Up Care: Monitoring response to treatment, assessing for complications, and providing counseling on contraception and prevention of future STIs.