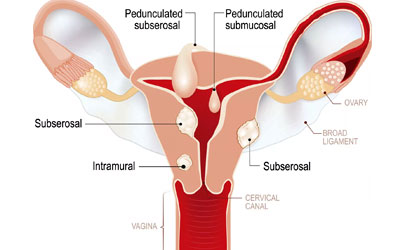
Fibroid
Fibroids, also known as uterine fibroids or leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. Depending on their size, number, and location, fibroids can cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, and reproductive issues. Gynecologists offer specialized services for the medical and surgical management of fibroids.
Medical Management of Fibroids
Medical management involves using medications to alleviate symptoms associated with fibroids and sometimes to reduce the size of the fibroids themselves.
Gynecological Services:
- Symptom Management: Prescribing medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and discomfort caused by fibroids.
- Hormonal Treatments: Using hormonal therapies such as birth control pills, hormonal IUDs (intrauterine devices), or GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) agonists to shrink fibroids and reduce symptoms.
- Tranexamic Acid: Prescription of medications like tranexamic acid to lessen heavy menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
- Expectant Management: Monitoring fibroids without immediate intervention, particularly if symptoms are mild or if nearing menopause when fibroids may shrink naturally.
Surgical Management of Fibroids
1. Surgical Management by Open Surgery:
Open surgery for fibroids involves making an incision in the abdomen (similar to abdominal hysterectomy) to access and remove fibroids or perform other surgical procedures to manage symptoms.
Gynecological Services:
- Indications: Used for large fibroids, multiple fibroids, or when preservation of the uterus or fertility is desired.
- Procedure: Surgeons remove fibroids (myomectomy) while preserving the uterus or perform a hysterectomy if necessary. This approach allows direct visualization and management of all fibroids and other pelvic organs.
- Recovery: Longer recovery time compared to minimally invasive procedures, with a hospital stay typically required and a longer period of postoperative care.
2. Surgical Management by Laparoscopy (Minimally Invasive):
Laparoscopic surgery for fibroids involves using small incisions and specialized instruments, guided by a camera (laparoscope), to access and remove fibroids or perform other surgical procedures.
Gynecological Services:
- Indications: Suitable for smaller fibroids, fewer fibroids, or when preserving fertility is desired.
- Procedure: Surgeons use laparoscopic instruments to remove fibroids (laparoscopic myomectomy) or perform other procedures such as laparoscopic hysterectomy if needed.
- Advantages: Shorter hospital stay, faster recovery time, reduced postoperative pain, and smaller scars compared to open surgery.
- Skill Requirement: Requires specialized training and expertise in laparoscopic techniques for optimal outcomes.
Considerations and Follow-Up
- Patient Counseling: Gynecologists provide detailed information about each treatment option, discussing benefits, risks, and potential impact on fertility and overall health.
- Postoperative Care: Monitoring patients closely after surgery, managing pain, and providing instructions for postoperative care and recovery.
- Long-Term Management: Addressing any concerns or complications post-surgery, including hormonal changes, and providing follow-up care as needed.