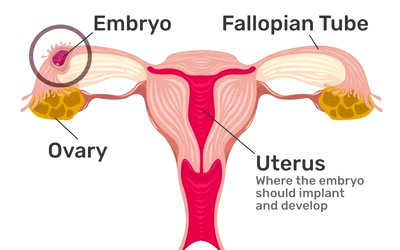
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and develops outside the uterus, typically in one of the fallopian tubes. This condition requires prompt medical attention as it can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
Components of Gynecological Services for Ectopic Pregnancy:
1. Diagnosis:
- Symptoms Assessment: Recognizing symptoms such as abdominal pain (often severe and one-sided), vaginal bleeding, shoulder pain (due to internal bleeding), and dizziness or fainting.
- Physical Examination: Conducting a pelvic exam to check for tenderness or masses in the abdomen.
- Ultrasound: Performing transvaginal ultrasound to visualize the location of the pregnancy and confirm if it is ectopic.
2. Management and Treatment:
- Monitoring and Observation: In cases where the ectopic pregnancy is small and stable, close monitoring with serial blood tests (beta-hCG) and ultrasound may be recommended.
- Medications: Administering methotrexate, a medication that stops the growth of the developing embryo and allows the body to reabsorb it, especially if the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and there is no rupture.
- Surgery: Performing laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive) or open surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair any damage to the fallopian tube if it has ruptured or is at risk of rupturing. This may involve salpingectomy (removal of the affected fallopian tube) or salpingostomy (removal of the pregnancy while preserving the tube).
3. Follow-Up Care:
- Recovery Monitoring: Monitoring the patient’s recovery post-treatment, ensuring that hCG levels decrease appropriately and symptoms resolve.
- Emotional Support: Providing emotional support and counseling for patients and their families, as ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally challenging.
4. Fertility Counseling:
- Assessment: Evaluating the impact of ectopic pregnancy and its treatment on future fertility.
- Education: Discussing the risks of recurrent ectopic pregnancy and options for achieving pregnancy in the future, including assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as IVF.
5. Prevention Strategies:
- Education: Providing information about risk factors for ectopic pregnancy, such as previous ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgeries, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
- Family Planning: Offering counseling on contraception options and the importance of early detection and prompt treatment of pregnancies to minimize the risk of ectopic pregnancy.